Streamflow forecast in the Manuel Alves da Natividade watershed using SARIMA time series model
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.20873/jbb.uft.cemaf.v7n4.duarteKeywords:
hydrological simulation, hydrology, water flow, time seriesAbstract
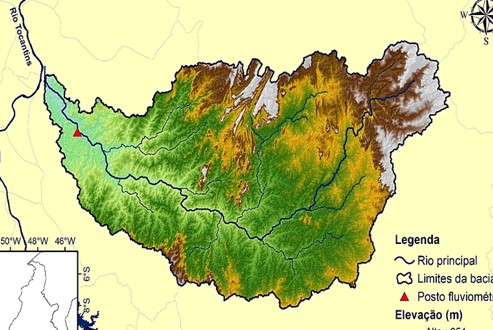
Streamflow knowledge and modeling is fundamental for water resources management. Hydrologic models help on water supply planning and projects regarding water budget, hydropower generation, irrigation systems, sustainable use and biodiversity conservation. The study area is Manuel Alves da Natividade (BHMAN) watershed, located in the Tocantins-Araguaia river basin. The BHMAN is one of the main tributaries of the Tocantins river. In this context, the objective was to analyze, model and make predictions of the surface runoff based on the time series model SARIMA, with monthly step. The methodology adopted was that of Box and Jenkins which consists of: identifying the model; estimate their parameters and apply the adjusted model for forecasting. The streamflow series was verified for its trend, seasonality and stationarity. The identification of the component orders of the models was made through the graphical analysis of the correlograms and periodograms. The selection of the best model was performed based on the selection criteria and quality measures. The model chosen was the SARIMA(1,0,1)(1,1,4)12, which presented Nash-Sutcliffe coefficients of 0.61 and 0.81 for the calibration and validation steps, respectively, which are considered good according to the classification applied for conceptual hydrological models. The model proved good performance in predicting hydrography recession, being indicated mainly as a tool for water resources management, irrigation planning and water supply.
References
AKAIKE, H. A bayesian analysis of the minimum AIC proce-dure. Ann Inst Stat Math, v.30, n.1, p.9–14, 1978.
AKAIKE, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, [s.l.], v.19, n.6, p.716-723, 1974.
ALMEIDA, L.; SERRA, J. C.V. Modelos hidrológicos, tipos e aplicações mais utilizadas. Revista da FAE, v.20, n.1, p.129-137, 2017.
ANA. Agência Nacional de Águas. Ministério do Meio Am-biente (Org.). Conjuntura dos recursos hídricos no Brasil 2018: informe anual. Brasília: ANA, 72p. 2018.
BATISTA, A.L.F. Modelos de séries temporais e redes neu-rais artificiais na previsão de vazão. Ano de obtenção: 2009. 79p. Dissertação (Mestrado em engenharia de sistemas) - Universidade Federal de Lavras, Lavras, Minas Gerais.
BAYER, D.M.; CASTRO, N.M.R.; BAYER, F.M. Modela-gem e previsão de vazões médias mensais do rio Potiribu utilizando modelos de séries temporais. Revista Brasileira de Recursos Hídricos, v.17, p.229-239, 2012.
BAYER, F.M., SOUZA, A.M. Wavelets e modelos tradicio-nais de previsão: um estudo comparativo. Revista Brasileira de Biometria, v.28, n.2, p.40–61, 2010.
BLEIDORN, M.T.; PINTO, W.P.; BRAUM, E.S.; LIMA, G. B.; MONTEBELLER, C.A. Modelagem e previsão de va-zões médias mensais do rio Jucu, ES, utilizando o modelo SARIMA. IRRIGA, v.24, n.2, p.320-335, 2019.
BOX, G.E.; JENKINS, G.M.; REINSEL, G.C.; LJUNG, G.M. Time series analysis: forecasting and control. John Wiley & Sons, 2008.
CALDEIRA, T.L. Aprimoramento computacional do modelo Lavras Simulation of Hydrology (LASH). Ano de obtenção: 2016. 213 p. Dissertação (Mestrado em Recursos Hídricos) - Universidade Federal de Pelotas, Pelotas.
CHECHI, L.; BAYER, F.M. Modelos univariados de séries temporais para previsão das temperaturas médias mensais de Erechim, RS. Revista Brasileira de Engenharia Agrícola e Ambiental-Agriambi, v.16, n.12, 2012.
DHOTE, V.; MISHRA, S.; SHUKLA, J. P.; PANDEY, S.K. Runoff prediction using big data analytics based on ARIMA model. Indian Jounal of Geo Marine Sciences, v.47, n.11, p.2163-2170, 2018.
DICKEY, D.A.; FULLER, W.A. Distribution of the Estima-tors for Autoregressive Time Series with a Unit Root. Jour-nal of the American Statistical Association, v.74, n.366a, p.427-431, 1979.
FIGUEIREDO, N.M., BLANCO, C.J.C. Simulação de vazão e níveis de água médio mensais para o rio Tapajó usando modelos ARIMA. Revista Brasileira de Recursos Hídricos, v.19, n.3, p.111–126, 2014.
GÓMEZ, V.; MARAVALL, A. Estimation, prediction, and interpolation for nonstationary series with the Kalman filter. Journal of the American Statistical Association, v. 89, n.426, p.611-624, 1994.
GOTSCHALK, L.; BATCHVAROVA, E.; GRYNING, S. E.; LINDROTH, A.; MELAS, D.; MOTOVILOV, Y. U. G.; FREEH, M.; HEIKINHEIMO, M.; SAMUELSSON, P.; GRELLE, A.; PERSSON, T. Scale aggregation: Com-parison of flux estimates from NOPEX. Jounal of Agricul-tural and Forest Meteorology, v.98-99, p.103-120, 1999.
HAO, C.-F.; QIU, J.; LI, F.-F. Methodology for Analyzing and Predicting the Runoff and Sediment into a Reservoir. Water, v.9, n.6, p.440, 2017.
HYNDMAN, R. J.; ATHANASOPOULOS, G. Forecasting: principles and practice, 2nd edition, Melbourne: OTexts. 2018.
Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais - INPE. Disponível em: <http://www.dsr.inpe.br/topodata/>. Acesso em: 20 de setembro de 2012.
LJUNG, G. M.; BOX, G. E. P. On a measure of lack on fit in time series models. Biometrika. v.65, n.2, p.297-303, 1978.
MACHEKPOSHTI, K.H.; WEDGHI, H.; TELVARI, A.; BABAZADEH, H. Flood Predicting in Karkheh River Ba-sin Using Stochastic ARIMA Model. International Journal of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering, v.12, n.3, p.89-96, 2018.
MIRANDA, N. M.; CATALDI, M.; SILVA, F. N. R. Simu-lação do regime hidrológico da cabeceira do rio São Francis-co a partir da utilização dos modelos SMAP e RegCM. Anuário do Instituto de Geociencias, v.40, n.3, 2017.
MISHRA S.; SARAVANAN, C.; DWIVEDI, V.K.; SHUKLA, J.P. Rainfall-runoff modeling using clustering and regression analyses for the river Brahmaputra basin. Journal Geological Society of India, v.92, n.3, p.305-312, 2018.
MORETTIN, P.; TOLOI, C. Análise de Séries Temporais. São Paulo: ABE - Projeto Fisher – Blucher, 2006.
MORIASI, D.N.; ARNOLD, J.G.; LIEW, M.W. VAN; BINGER, R.L.; HARMEL, R.D.; VEITH, T. Model eval-uation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Transactions of the ASABE, v.50, n.3, p.885-900, 2007.
PEREIRA, D.R.; ULIANA, E.M.; MARTINEZ, M.A.; SIL-VA, D.D. Desempenho de um modelo hidrológico concen-trado e de um semidistribuído na predição de vazões diárias. Irriga, v.21, n.2, p.409-409, 2016.
R Development Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Com-puting, Vienna, Austria, 2014. URL http: //www.R-project.org, ISBN 3-900051-07-0.
REISEN, V.A., MOLINARES, F.A.F., TEIXEIRA, E.C. Modelagem de séries temporais sazonais na presença de ou-tliers: estudo de caso da vazão máxima mensal do rio Jucu, ES, Brasil. Revista Brasileira de Recursos Hídricos, v. 13, n. 2, p. 45–53, 2008.
RODRIGUES, J. A. M.; ANDRADE, A. C. O.; VIOLA, M. R.; MORAIS, M. A. V. Indicadores hidrológicos para a gestão de recursos hídricos na bacia hidrográfica do rio Ma-nuel Alves da Natividade, Tocantins. Scientia Agraria, v.16, n.4, 2015.
SANTOS, P.G.P.; OLIVEIRA, T.F. Modelagem e previsão de vazão afluente média mensal no Rio Tocantins, Usina Hidrelétrica Tucuruí-Pará, Amazônia, Brasil. Biota Amazônia, v.6, n.2, p.9-16, 2016.
SHAPIRO, S.S.; WILK, M.B. An analisy of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika, v.52, p.591-611, 1965.
TEODORO, V.A. Comparação de método de imputação para dados de precipitação diária. Ano de obtenção: 2019. 85 p. Tese (Doutorado) - Escola Superior de Agricultura “Luiz de Queiroz”. Piracicaba.
TUCCI, C.E.M. Modelos hidrológicos. Porto Alegre: Editora da UFRGS, 1998.
ULIANA, E.M.; PEREIRA, D.R; SILVA, D.D.; ALMEIDA, F.T.; SOUZA, A.P. Modelagem chuva-vazão em uma bacia tropical utilizando o modelo IPH II. Geo Uerj, n.33, 2018.
UNESCO. United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization. The united nations world water development report: Managing Water under Uncertainty and Risk, 2015.
VALLADARES NETO, J.; SANTOS, C.B.; TORRES, E.M.; ESTRELA, C. Boxplot: um recurso gráfico para a análise e interpretação de dados quantitativos. Revista Odontológica do Brasil Central, v.26, n.76, p.1-6, 2017.
VIANA, J.F.S.; MONTENEGRO, S.M.G.L.; SILVA, B.B.; SILVA, R.M.; SOUSA, W.S. Modelagem hidrológica da bacia hidrográfica do rio Pirapama-PE utilizando o modelo SWAT. Journal of Environmental Analysis and Progress, v.3, n.1, p.155-172, 2018.
VIOLA, M.R.; MELLO, C.R.; ACERBI JUNIOR, F.W.; SILVA, A.M. Modelagem hidrológica na bacia hidrográfica do rio Aiuruoca, MG. Revista Brasileira de Engenharia Agrícola e Ambiental, v.13, n.5, p.581-590, 2009.
WEI, W. Time Series Analysis: Univariate and Multivariate Methods. New York: Addison Wesley, 2006.
XUE, L.; YANG, F.; YANG, C.; WEI, G.; LI, W.; HE, X. Hydrological simulation and uncertainty analysis using the improved TOPMODEL in the arid Manas River basin, Chi-na. Scientific reports, v.8, n.1, p.452, 2018.
ZAPPA, M. Multiple-response verification of a distributed hydrological model at different spatial scales. Ano de obten-ção: 2002. 157p. Tese (Pós-doutorado). Swiss Federal Insti-tute of Technology. Switzerland.
ZHANG, Q.; WANG, B-D.; HE, B.; PENG, Y.; REN, M-L. Singular spectrum analysis and ARIMA hybrid model for anual runoff forecasting. Water Resour Manage, v. 25, n. 11, p. 2683-2703, 2011.
ZHAO, X.; CHEN, X.; XU, Y.; XI, D.; ZHANG, Y.; ZHENG, X. An EMD-based chaotic least squares support vector machine hybrid model for annual runoff forecasting. Water, v.9, n.3, p.153, 2017.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 - Journal of Biotechnology and Biodiversity

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0 at http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g. in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (Available at The Effect of Open Access, at http://opcit.eprints.org/oacitation-biblio.html).


